Treamis international school in Bangalore
Primary School (IB-PYP)
Treamis International School (TIS) offers IB-PYP programs in the primary school. It offers the Cambridge Lower Secondary curriculum in the middle school. In the high school, it offers IGCSE and International A Level programs from the Cambridge Assessment International Examination. Treamis International School is a Center for Cambridge Examinations.
TIS is an IBDP candidate school. The program will commence from 2022 academic year.


TIS – Primary Years Programme
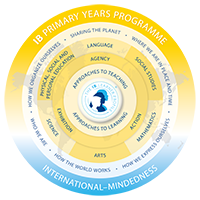
The IB Primary Years Programme starts at age 3 when the child enters pre-kindergarten. At the primary level, children are developed into inquiring, knowledgeable and caring young people with adaptable skills so they can face society’s complex challenges. The key features of the programme are:
- Creating tomorrow’s global citizens. The programme emphasizes the IB learner profile attributes and the approaches to learning for the development of international-mindedness.
- Inquiry-based approach: The mentors facilitate connecting children to new information by activating their prior knowledge. They also help in connecting children’s knowledge to concepts and personal experiences in meaningful ways.
- Transdisciplinary themes: The subject areas from maths to library are taught through transdisciplinary themes. With this approach the students learn to make connections between the subjects and with the outside world as well.

Kindergarten
Kindergarten at Treamis – The perfect balance of learning and play
Pre-Kindergarten (Age 3-4 years)
Pre-kindergarten classes offer endless opportunities for children to meet success every day.
As the first school of experience, the child is provided an environment that fosters self-esteem and a genuine love of learning. Circle time with music and movement is combined with dramatic play, art, building blocks, fine motor manipulatives and science and sensory areas help children grow in all areas of development. A sense of wonder is introduced through science units as the children explore the world. Outside, gross motor play provides fun and positive social interactions.
Lower Kindergarten (Age 4-5 years)
The children recognize letters and some letter sounds, add two groups of concrete objects by counting and begin to understand the concept of yesterday, today and tomorrow.
They continue their growth in language and social development as they learn classroom expectations and procedures. Children acquire STEM skills associated with math and science. Understanding of numbers and shapes, hypothesizing, investigating, measuring, drawing conclusions are all acquired through a play-based learning environment.
Upper Kindergarten (Age 5-6 years)
The children acquire foundational literacy and math skills. They learn letter-sound relationships, sight word recognition and basic mathematical functions. They also undergo a character education program which nurtures important social and emotional skills such as listening, understanding feelings and resolving conflicts. Fine motor development and creativity is learned through art projects. All this in addition to building community, learning valuable conflict resolution skills and developing relationships makes this class a perfect transition to Grade 1.
The Kindergarten is a full day program, the specialist and homeroom classes take place in the morning. In the afternoon, after lunch and a nap the children are engaged in various indoor and outdoor activities.


Grades 1-5
The students study the following subjects in their primary years from Grade 1–5
Language
- Oral —listening and speaking
- Visual —viewing and presenting
- Written – reading and writing
Languages taught
- English
- Hindi/French (2nd language options)
- Kannada (Regional language study)
Mathematics
- Data handling
- Measurement
- Shapes and space
- Pattern and function
- Number
Science
- Living things
- Earth and space
- Materials and matter
- Forces and energy
Social Studies
- Human systems and economic activities
- Social organization and culture
- Continuity and change through time
- Human and natural environments
- Resources and the environment
Information & Communication Technologies (ICT)
- Learn to use a wide range of digital tools, media and learning environments
- Learn to investigate, create, communicate, collaborate, organize and be responsible for their own learning and actions.
- Learn to make connections and understand its relevance and applicability in everyday lives.
- Develop and apply strategies for critical and creative thinking, engage in inquiry and apply new understandings and skills in different contexts.
Library
- Use resources from the library such as collections of fiction, non-fiction, magazines, and research materials to enhance learning.
- Borrow books from the library and read at home along with parents.
Personal, Social & Physical Education
Physical Education Programme
The objectives of the programme are to
- Reinforce sport techniques in speed of execution, precision, and power.
- Bring awareness on the benefits of a healthy lifestyle and the importance of physical activity in daily lives.
- Bring awareness of space, direction and levels in relation to others and their environment.
- Develop basic skills involving agility, flexibility, strength, response and coordination.
- Diversify, refine, combine and link the acquired skills into more advanced tactics and strategies.
- Combine the movements to create sequences refining basketball, soccer, volleyball, yoga/taekwondo, athletics skills.
The programme focuses on Fun/action – acceptance, participation, connect with self and earth for Grades 1 & 2. For Grades 3 – 5, the focus is on skill building, teams, moral values, develop and become good human being.
Physical activities:
- Fitness (All Grades)
- Fundamental Movements (Grade -1-2)
- Adventure Activities (Grade – 1-2)
Team sports:
- Basketball (Grade 3 – 5)
- Soccer (Grade 3 – 5)
- Volleyball (Grade 3 – 5)
Individual sports:
- Athletics (Grade 3 – 5)
- Swimming (Grade 1 – 5)
- Yoga (Grades 1 – 5)
Performing Arts
Dance
- Exploring dances, gaining both a physical and theoretical understanding
- Individual investigation
- Developing creative aspect of making dances; composing original work
- Movement skills appropriate to the dancer’s performance
- Clarity in relationship to space, time, dynamics and movement qualities appropriate to the work
- Communicative expression in relation to other performers and to the audience
Music
- Singing and movement through the study of melody and rhythm
- Developing reading and simple notation skills.
- Singing, playing instruments, listening, reading and writing music through the study of melody, rhythm, harmony and form.
- Songs and compositions from around the world.
Visual Arts
- Focus on the elements of art and the creative process.
- Explore a wide variety of materials and tools.
- Exposure and response to artifacts and artwork of varied origins and reflect on self and others artwork.
- Self-awareness about one’s interest and preferences in art.
- Aware of the elements and principles of art and design
- Make independent choices about tools, media and materials appropriate for one’s artwork.
- Examine artwork and artifacts from different periods and make predictions about their function.
- Reflect on one’s own work and the work of others with sensitivity and appreciation.
Reporting & Demonstration of Knowledge
Reporting & Demonstration of Knowledge
Demonstration of the knowledge acquired and their reporting are done in the following ways.
Parent/teacher/student Conferences: During the conference held twice a year, the homeroom mentor and the subject teachers provide detailed progress of the students. Evidence from the classroom work is used to set goals and action items for parents, students and the teachers.
Student-led conferences: In this conference conducted once a year by the students, parents understand and appreciate the knowledge acquired not only by their children but also by other students. Students lead parents through a discussion of their work and established academic and social goals. The student directs the conversation focused on their work and classroom behavior. The classroom mentor does not participate directly in the conference except to facilitate the event.
Pinnacle Day: Children celebrate their learning with a whole new perspective during the Pinnacle Day conducted twice a year. They demonstrate their knowledge with performances and presentations.
Progress and Performance Reports: Parents receive written reports about their children six times a year at the end of each term. The reports document progress in relation to units of inquiry and stand-alone subjects, the learner profile attributes, attitudes and skill development.
In their final year ie., Grade 5, the students carry out an extended, in-depth, collaborative project known as the PYP exhibition. This involves students working collaboratively to conduct an in-depth inquiry into real life issues or problems. Students collectively synthesise all of the essential elements of the Primary Years Programme in ways that can be shared with the whole school community. The event also provides teachers with a powerful and authentic process for assessing student understanding.
The exhibition represents a unique and significant opportunity for students to exhibit the attributes of the IB learner profile developed throughout their engagement in PYP. It also provides schools and students with a wonderful opportunity to celebrate the transition of learners to the next phase of their education.
Parent – Teacher Meetings: Parents or a teacher can initiate a meeting at a time convenient to each other to address any specific issue of concern with the student. During this meeting, goals are set and action items are documented


CLS – Cambridge Lower Secondary (Grades 6-8)
The Cambridge Lower Secondary program is designed for students approximately 11 -14 years old. It builds on the PYP program in the primary school at Treamis and develops children’s knowledge and skills in Mathematics, English and Science. The lower Secondary provides standardized tests to allow careful monitoring of progress from primary to lower secondary phases. It also provides excellent preparation for students embarking on IGCSE or O level courses.
- Languages:
- English
- French
- Hindi
- Sanskrit
- Mathematics
- Science
- Social Science
- Information & Communication Technology
- Art & Design
- Physical Education:
- Basketball
- Soccer
- Swimming
- Yoga
- Performing Art:
- Dance
- Music
Checkpoint
IGCSE Program (Grades 9 & 10)
The inquiry into every aspect of the learning and the application of the concepts learned at IGCSE provides a foundation for higher level courses including AS and A levels. Extending the IGCSE programme with additional subjects will lead to AICE diploma.
The curriculum consists of a two years course of study leading to an examination which is typically taken at the end of Grade 10. Students can get entry into Universities / Colleges in some countries on obtaining exceptional grades at IGCSE.
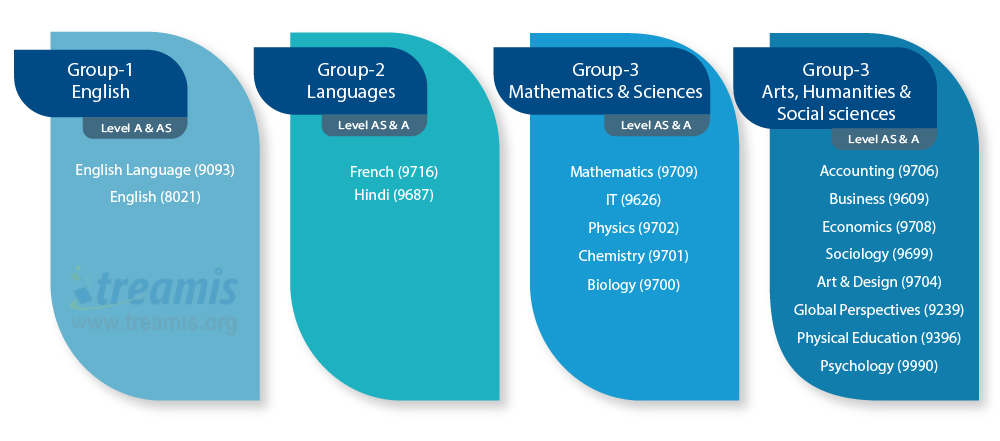
Subjects offered at Treamis in IGCSE

Assessment for Cambridge IGCSE includes written & oral tests and practical examinations. Treamis considers both examinations as well as coursework for assessing the students. The subject teacher sets and grades the coursework which is moderated by CAIE.
International Certificate of Education (ICE) Award
- Two subjects from the language group.
- One from each of the other four groups.
- One more from any of the five groups.
Students who qualify for the Cambridge ICE award will be placed in one of three categories:
- Distinction –– Grade A or better in five subjects and grade C or better in two subjects.
- Merit– Grade C or better in five subjects and grade F or better in two subjects.
- Pass– Grade G or better in seven subjects.
An important benefit that Cambridge ICE offers is that students can demonstrate competence across a wide range of subjects and skills. Cambridge ICE carries greater currency in its own right in those countries where it is popular.
TIS – A Level
A level is a two-year program from CAIE after the completion of IGCSE. It provides a strong foundation for University education and is accepted as a proof of academic ability by the Universities all over the world. An A Level course is probably the most in-depth and thorough preparation for university, medical college or employment that a school can give its students.
The A Level is a 2-year program at Treamis. The subject content of each A Level syllabus has been subdivided into two parts
A level examinations are equivalent to 12th standard examinations of other curriculum Boards in India. Students should have completed tenth grade or its equivalent in order to be eligible for enrolment in AS Level.
Subjects offered at Treamis in AS & A Levels
Advanced Subsidiary Level:
The AS level is awarded to the candidate who clears minimum four subjects including subjects from Group 1 and any three from the remaining options.
Students enrolling in Mathematics should choose a specialization subject from the following.
- Mathematics, Mechanics
- Mathematics, Probability and Statistics
- Mathematics extended Mathematics.
Mathematics together with a specialization subject makes one whole unit.
Advanced Level:
The A2 level is awarded to the candidate who clears a minimum of any three subjects from the above options.
Students enrolling in Mathematics should choose a specialization subject from the following.
- Mathematics, Mechanics, Probability and Statistics.
- Mathematics, Mechanics, extended Mechanics
- Mathematics, Probability and Statistics, extended Probability and Statistics.
- Mathematics together with a specialization subject makes one whole unit.
Parents and students should check the minimum subject requirements (prerequisites) of the Universities and the departments they plan to seek admission after the completion of A Level. Choosing the right subjects will help them achieve their academic & career goals.
Diploma:
An A Level would count as a double-credit qualification and an AS Level as a full (single) credit course within the Cambridge AICE Diploma award framework.
Structured approach to obtaining Diploma:
- Take all A Level components in the same examination session at the end of the course of study, most normally the end of the second year
- Follow a staged assessment to A Level by taking the Advanced Subsidiary qualification in one examination session, and the final part of assessment in a subsequent session
- Take the AS Level only
The structure of the International A Level is such that co-teaching of students following both AS and A Level routes is possible.
TIS – AS Level
Advanced Subsidiary Level:
The AS level is awarded to the candidate who clears minimum four subjects including subjects from Group 1 and any three from the remaining options.
Students enrolling in Mathematics should choose a specialization subject from the following.
- Mathematics, Mechanics
- Mathematics, Probability and Statistics
- Mathematics
Mathematics together with a specialization subject makes one whole unit.
Advanced Level:
The A2 level is awarded to the candidate who clears a minimum of any three subjects from the above options.
Students enrolling in Mathematics should choose a specialization subject from the following.
- Mathematics, Mechanics, Probability and Statistics.
- Mathematics, Mechanics, extended Mechanics
- Mathematics, Probability and Statistics, extended Probability and Statistics.
- Mathematics together with a specialization subject makes one whole unit.
Choosing the subjects:
Parents and students should check the minimum subject requirements (prerequisites) of the Universities and the departments they plan to seek admission after the completion of A Level. Choosing the right subjects will help them achieve their academic & career goals.
Diploma:
An A Level would count as a double-credit qualification and an AS Level as a full (single) credit course within the Cambridge AICE Diploma award framework.
Structured approach to obtaining Diploma:
- Take all A Level components in the same examination session at the end of the course of study, most normally the end of the second year
- Follow a staged assessment to A Level by taking the Advanced Subsidiary qualification in one examination session, and the final part of assessment in a subsequent session
- Take the AS Level only
The structure of the International A Level is such that co-teaching of students following both AS and A Level routes is possible.
TIS – IBDP
IB Diploma students study six courses at higher level or standard level. In addition the program has three core requirements that are included to broaden the educational experience and challenge students to apply their knowledge and understanding.
- The Extended Essay is a requirement for students to engage in independent research through an in-depth study of a question relating to one of the subjects they are studying.
- Theory of Knowledge is a course designed to encourage each student to reflect on the nature of knowledge by critically examining different ways of knowing (perception, emotion, language and reason) and different kinds of knowledge (scientific, artistic, mathematical and historical).
- Creativity, Activity, Service (Creativity, Activity, Service) requires that students actively learn from the experience of doing real tasks beyond the classroom. Students can combine all three components or do activities related to each one of them separately. In addition, students are required to create and complete a CAS project of their own design.
